DISK SCHEDULING
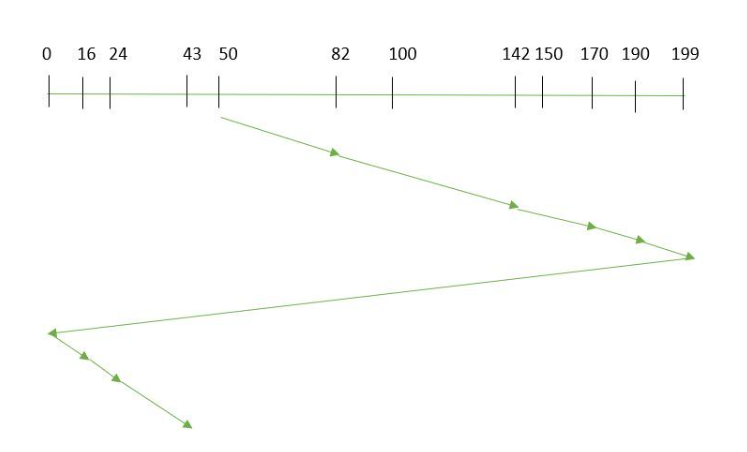
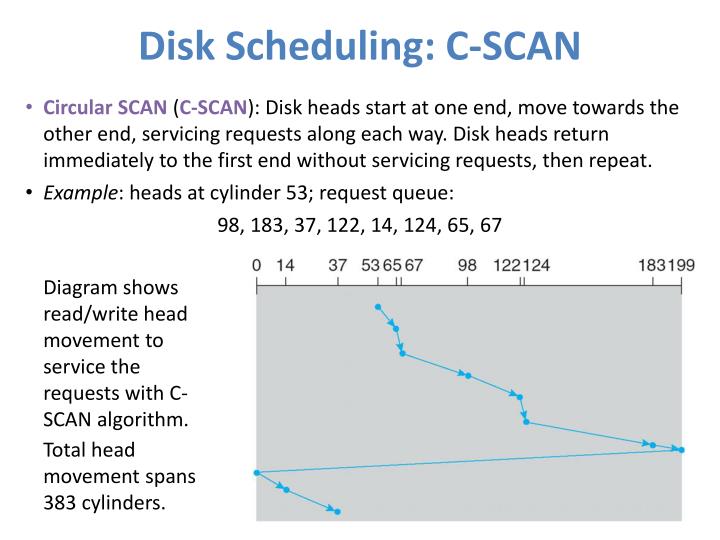
C-SCAN
The C-SCAN (Circular SCAN) disk scheduling algorithm improves disk performance by eliminating unnecessary back-and-forth head movement. It scans the disk in a single direction, servicing requests along the way, and quickly returns to the opposite end without servicing any requests. This circular pattern ensures consistent wait times for all requests and prevents stranded requests. C-SCAN is suitable for systems that require fair treatment and minimized wait time variations. It enhances efficiency by reducing unnecessary head movement and provides a consistent experience for all disk requests.
C-SCAN
Example: Suppose the requests to be addressed are-82,170,43,140,24,16,190. And the Read/Write arm is at 50, and it is also given that the disk arm should move “towards the larger value”.
ALGORITHM
Let Request array represents an array storing indexes of tracks that have been requested in ascending order of their time of arrival. ‘head’ is the position of disk head. The head services only in the right direction from 0 to the size of the disk. While moving in the left direction do not service any of the tracks. When we reach the beginning(left end) reverse the direction. While moving in the right direction it services all tracks one by one. While moving in the right direction calculate the absolute distance of the track from the head. Increment the total seek count with this distance. Currently serviced track position now becomes the new head position. Go to step 6 until we reach the right end of the disk. If we reach the right end of the disk reverse the direction and go to step 3 until all tracks in the request array have not been serviced.